Understanding the basic financial terms is required to assess market trends, make informed decisions, manage risks and finances, and, most importantly, forecast and plan. So, entrepreneurs, any business personnel, or, in fact, every common person in the current commerce-oriented world must have the ability to understand and assess financial terms.
How do people achieve Financial Freedom?
Seven Financial Terms Explained for Part-1
Below is the first batch of seven financial terms explained in part 1.
1. Business Cycle
Business cycle is among key financial terms for entrepreneurs, especially for newbies. The business cycle is the rise and fall of a nation’s economic activity. It shows fluctuations in aggregate economic output and employment over time. A business cycle typically consists of four phases: Expansion, Peak Contraction, and Trough.
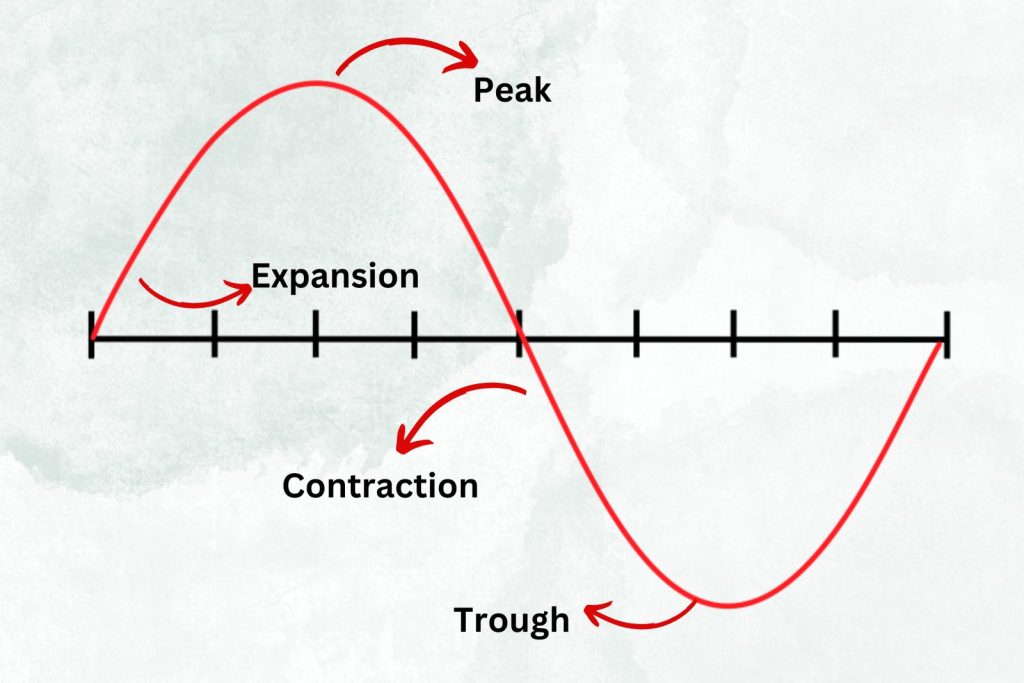
a. Economic Expansion
Economic expansion is the upward movement in the business cycle towards the peak. This upward swing of the business cycle is associated with increased economic output, wages, and consumer spending. Economic activity or business starts booming in this phase.
Learn various aspects of Financial Literacy
b. Peak
Peak is the second stage in the business cycle, where the economy reaches its saturation point. It is the highest point at which economic activity reaches its highest levels; aggregate output and employment reach the maximum level, and further growth of economic indicators stops.
c. Economic Contraction
Economic contraction is the downward movement in the business cycle towards the trough. This downward business cycle swing is associated with decreased economic output, wages, and consumer spending.
Economic impacts of Climate Change
d. Trough
The trough in the business cycle is the lowest point at which economic activity reaches its lowest levels, economic rates become negative, and the economy reaches a negative saturation point. At this point, a significant decline in national income and expenditure occurs.
Some Sever Cases of Business Cycle
Boom is the most robust expansion in the economic activity where businesses operate at total capacity, and at the same time, income and production (output) reach maximum level. This phase is marked by high consumer confidence and strong and healthy financial markets.
How US dollar became so powerful?
Recession is a significant and prolonged decline in economic activity that lasts for extended periods, marked by a decrease in output, employment, and key financial indicators. It is marked by a sustained negative growth that lasts from months to years.
Depression is a severe form of recession marked by a severe contraction in output and widespread unemployment. Financial distress, a banking crisis, and a significant decline in consumer and business confidence mark it.
Which are the most powerful currencies in 2024?
2. Balance of Payment
Balance of payments (BOP) is a method countries use to monitor all international transactions with the rest of the world for a given period. These transactions include imports and exports of goods, services, financial assets, and transfer payments like foreign aid. The balance of payment comprises three components: the current account, capital account, and financial account.

a. Current Account
It is a component of the balance of payment that records the transactions of goods and services for a specific period. The current account is further divided into the following subaccounts:
Understanding and importance of Emergency Funds
Trade Balance: It is an essential component of the current account. It gives the difference between the monetary value of a country’s exports and imports for a given period. A positive trade balance means a trade surplus and a negative trade balance means a trade deficit.
Services: It refers to the exchange of intangible goods or services between countries. It includes transactions related to transportation, tourism, and other business services like financial services, education and healthcare services, information and communication technology services, etc.
Income and Unilateral Transfer: The income account involves income earned by investing abroad and income earned by foreign entities in the reporting country. On the other hand, unilateral transfers involve the transfer of grants, aids, or gifts unilaterally.
Note: A current account surplus is a condition where a country’s exports are more than imports. In contrast, a current account deficit is when a country imports more than exports.
Understand about investing in dividend stock
b. Capital and Financial Account
The capital and financial account are integral parts of a country’s balance of payments and reflect its trade with the rest of the world.
Capital accounts record non-financial transactions, such as the transfer of ownership of unproduced goods, and non-financial transactions, such as patents or copyrights. It shows the change of the country’s wealth through the exchange of valuable and intangible assets.
On the other hand, financial accounts record transactions related to financial assets and liabilities. This account includes FDIs, portfolio investments, and other financial instruments. Financial accounts are essential for understanding cross-border financial flows and assessing a country’s external financial situation.
3. Comparative Advantage
It is an economic concept that David Ricardo (a British Economist) proposed. This concept means that in a trade between two countries, both countries can get maximum benefits from trade by focusing on the production of goods or services they are good at producing while purchasing goods or services from other countries in which they are not as good for making it. In a nutshell, comparative advantage is the country’s economic ability to produce goods and services at lower opportunity costs than another country (trading partner).
Explore various investment markets
4. Absolute Advantage
Adam Smith, the Father of Modern Economics, developed this concept. This concept refers to the ability of a party (an individual, a company, or a country) to produce maximum output by using existing inputs and producing goods and services at a lower cost and more efficiently than other countries (competitors).
5. Budget Deficit
A budget deficit is a situation where total government spending (spending on public services, projects, etc.) exceeds government revenue, resulting in a negative balance. Here are 15 countries with highest budgets deficits for the year 2023.

Let’s say the government plans to improve its road network facilities in a country, and the government collects $10 billion in taxes, but the project cost is $12 billion. In this case, the country will face a budget deficit of $2 billion. However, the effect of this deficit is not harmful, but sometimes, it is needed to improve the collective socio-economic well-being of its citizens.
In contrast to the budget deficit, there is a concept called budget surplus; a budget surplus is a situation where total government revenue exceeds total government expenditure, resulting in a positive balance.
Explore the terms GDP and GNP, and the difference between them
6. Monetary Policy
Monetary policy is an economic policy used by central banks of countries to control the money supply and regulate macroeconomic indicators like inflation, unemployment, and exchange rates. This management is done through different tools like fluctuations in interest rates, buying and selling securities, and making loans. The primary function of monetary policy is to regulate inflation, influence the level of employment, and manage exchange rates.

Monetary policy can be divided into two types, i.e., Contractionary Monetary Policy and Expansionary Monetary Policy.
Contractionary Monetary Policy aims to reduce the amount of money in the economy. This can be done by increasing interest rates, selling government bonds, and growing bank reserve requirements. Central banks use this policy to control the levels of inflation.
What is money? Understand its aspects and types
Central banks use an Expansionary Monetary Policy to increase the money in an economy. This can be done by decreasing interest rates, buying government bonds, and decreasing bank reserve requirements. This policy aims to reduce unemployment and to stimulate economic growth.
8. Fiscal Policy
It is an economic policy that involves government decisions regarding taxation (the amount of money earned by the government through tax) and expenditure (the amount of money the government spends) to influence economic growth. The government uses Fiscal policy to stabilize economic growth and inflation and control unemployment. The government may increase spending or reduce taxes in a recession to control economic activity. Fiscal policy can also be divided into two types, i.e., Contractionary Fiscal Policy and Expansionary Fiscal Policy.
Why does paper currency losses value over time?
In Contractionary Fiscal Policy, the government reduces its spending. It increases the taxes in the country simultaneously, reducing aggregate demand and consumption and simultaneously reducing purchasing power. It is also one of the tools to control inflation.
In Expansionary Fiscal Policy, the government increases spending and lowers tax rates to boost economic growth. This results in more consumption due to an increase in purchasing power. Credit access for the business becomes easier; therefore, investment rises, and growth occurs.
Bottom Line
Understanding financial terms helps entrepreneurs equip themselves with relevant knowledge and skills that help them understand the complex business environment and can enhance their chances of business success. Moreover, this knowledge allows them to communicate effectively with the stakeholders and improves financial performance and their sustainability for long-term growth.








Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!